Bulk of Indonesia Data Hit by Cyberattack Not Backed Up, Officials Say
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Enlarge (credit: Getty Images)
Mac malware that steals passwords, cryptocurrency wallets, and other sensitive data has been spotted circulating through Google ads, making it at least the second time in as many months the widely used ad platform has been abused to infect web surfers.
The latest ads, found by security firm Malwarebytes on Monday, promote Mac versions of Arc, an unconventional browser that became generally available for the macOS platform last July. The listing promises users a “calmer, more personal” experience that includes less clutter and distractions, a marketing message that mimics the one communicated by The Browser Company, the startup maker of Arc.
According to Malwarebytes, clicking on the ads redirected web surfers to arc-download[.]com, a completely fake Arc browser page that looks nearly identical to the real one.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Prime Da7 2024 is almost here, and early Prime Day deals are going strong. Unsurprisingly, some of the best deals are for Amazon's own products, like this Blink Video Camera Bundle for $59.99 or this 4K Fire TV for $149.99.
If you're a Prime Member looking for a video doorbell deal and you wouldn't mind a free smart speaker too, consider this Blink Video Doorbell and Amazon Echo Pop Bundle, which will run you $34.99 (the same devices would cost $110 if purchased separately).
Blink is owned by Amazon, so it's no surprise to see the doorbell get a big Prime Day discount. However, it is surprising how much you'll get for your $35: The Blink Video Doorbell with the Sync Module 2 alone normally costs $69.99, and the Echo Pop normally goes for $39.99.
The Blink Video Doorbell can be wired or use batteries. It uses your phone as a chime bell, has two-way audio so that you can communicate with guests from your phone, and supports 1080p resolution and infrared night vision. The Sync Module 2 lets you control up to 10 Blink devices with your phone and use local storage for your video files instead of paying for cloud storage, but you'll need to buy a USB flash drive of up to 256 GB. Keep in mind that you will still need a Blink subscription to use all of Blink's features. The Blink subscription plan starts at $30 a year for Blink Basic.
The Echo Pop is Amazon's latest, most budget-friendly Echo smart speaker. It's an "excellent" smart speaker according to PCMag's review. One of its best features has nothing to do with the speaker abilities— if you use the Eero Mesh wifi system, the speaker doubles as a node to expand your wifi coverage.


A critical vulnerability recently discovered in a widely used piece of software is putting huge swaths of the Internet at risk of devastating hacks, and attackers have already begun actively trying to exploit it in real-world attacks, researchers warn.
The software, known as MOVEit and sold by Progress Software, allows enterprises to transfer and manage files using various specifications, including SFTP, SCP, and HTTP protocols and in ways that comply with regulations mandated under PCI and HIPAA. At the time this post went live, Internet scans indicated it was installed inside almost 1,800 networks around the world, with the biggest number in the US. A separate scan performed Tuesday by security firm Censys found 2,700 such instances.
Last year, a critical MOVEit vulnerability led to the compromise of more than 2,300 organizations, including Shell, British Airways, the US Department of Energy, and Ontario’s government birth registry, BORN Ontario, the latter of which led to the compromise of information for 3.4 million people.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
I've been covering Blink deals on Amazon for some time now, and have seen some good bundle deals before, but none compare to this one.
Right now, you can get a Blink Video Doorbell ($59.99 when bought by itself), a Blink Outdoor 4 camera ($99.99 purchased separately), and a Sync Module 2 ($49.99 purchased separately) for $59.99 with this Blink bundle. This is the lowest price the package deal has reached—by a long shot—according to price-checking tools.



You can also expand your coverage by adding two or three Blink Outdoor 4 cameras and still get a very good discount. This sale is part of Amazon's official early Prime Day deals, according to its press release, which also served as the official announcement that Prime Day 2024 will take place July 16-17.
This bundle has all the basics you need to set up your Blink security system. The Blink Video Doorbell has two-way audio so that you can communicate with guests from your phone, 1080p resolution, and infrared night vision. The Blink Outdoor 4 is the latest Blink outdoor camera and a great budget option that competes well with other outdoor cameras. The Sync Module 2 lets you use local storage for your video files instead of paying for cloud storage.
Note that you will need a Blink subscription to use all of this bundle's features. The Blink subscription plan starts at $30 a year for Blink Basic. For $100/year, you can get Blink Plus, which offers more features, including support for an unlimited number of devices.

Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Enlarge (credit: Getty Images)
WordPress plugins running on as many as 36,000 websites have been backdoored in a supply-chain attack with unknown origins, security researchers said on Monday.
So far, five plugins are known to be affected in the campaign, which was active as recently as Monday morning, researchers from security firm Wordfence reported. Over the past week, unknown threat actors have added malicious functions to updates available for the plugins on WordPress.org, the official site for the open source WordPress CMS software. When installed, the updates automatically create an attacker-controlled administrative account that provides full control over the compromised site. The updates also add content designed to goose search results.
“The injected malicious code is not very sophisticated or heavily obfuscated and contains comments throughout making it easy to follow,” the researchers wrote. “The earliest injection appears to date back to June 21st, 2024, and the threat actor was still actively making updates to plugins as recently as 5 hours ago.”
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

© Derek Abella
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Microsoft's latest Patch Tuesday update has a series of fixes for bugs in both Windows 10 and Windows 11. One of these vulnerabilities is particularly troubling though, as it allows bad actors to hack your PC so long as their within wifi range.
As reported by The Register, Microsoft patched 49 security flaws with its latest Patch Tuesday update, but there are really three of key interest: The first, which Microsoft says is public (but not exploited), is tracked as CVE-2023-50868 and can allow a bad actor to push your CPU to the point where it stops functioning correctly. The second, CVE-2024-30080, concerns Microsoft Message Queuing: This flaw allows a remote attacker to send a malicious data packet to a Windows system, and execute arbitrary code on that system. This one doesn't necessarily affect individual users as much, but Microsoft did give it a high severity rating, and while it hasn't necessarily been exploited yet, the company thinks exploitation is more than likely. But the last flaw seems most pressing: CVE-2024-30078 is a vulnerability affecting wifi drivers. The company says a bad actor can send a malicious data packet to a machine using a wifi networking adapter, which would allow them to execute arbitrary code. In practice, this could allow someone within wifi range of another user to hack their computer from that wifi connection alone. And since this affects many different versions of Windows, attackers will likely try to exploit this flaw as soon as possible.
It's a chilling concept: If someone learns how to exploit this flaw, they could use it to attack other Windows PCs in their immediate vicinity. Imagine the field day a hacker could have going to a high-density area of laptop users like a coffee shop or shared workspace. Fortunately, the latest security updates for both Windows 10 and Windows 11 patch these issues, so once you're updated, you're safe to return to your office in the corner of the café.
If you're running Windows 11, head to Start > Settings > Windows Update. On Windows 10, head to Start > Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update. Either way, hit Check for updates. Once available, download and install it on your PC.


Enlarge / Ford Mustang Mach E electric vehicles are offered for sale at a dealership on June 5, 2024, in Chicago, Illinois. (credit: Scott Olson / Getty Images)
CDK Global touts itself as an all-in-one software-as-a-service solution that is "trusted by nearly 15,000 dealer locations." One connection, over an always-on VPN to CDK's data centers, gives a dealership customer relationship management (CRM) software, financing, inventory, and more back-office tools.
That all-in-one nature explains why people trying to buy cars, and especially those trying to sell them, have had a rough couple of days. CDK's services have been down, due to what the firm describes as a "cyber incident." CDK shut down most of its systems Wednesday, June 19, then told dealerships that afternoon that it restored some services. CDK told dealers today, June 20, that it had "experienced an additional cyber incident late in the evening on June 19," and shut down systems again.
"At this time, we do not have an estimated time frame for resolution and therefore our dealers' systems will not be available at a minimum on Thursday, June 20th," CDK told customers.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Enlarge (credit: Getty Images)
Two men have pleaded guilty to charges of computer intrusion and aggravated identity theft tied to their theft of records from a law enforcement database for use in doxxing and extorting multiple individuals.
Sagar Steven Singh, 20, and Nicholas Ceraolo, 26, admitted to being members of ViLE, a group that specializes in obtaining personal information of individuals and using it to extort or harass them. Members use various methods to collect social security numbers, cell phone numbers, and other personal data and post it, or threaten to post it, to a website administered by the group. Victims had to pay to have their information removed or kept off the website. Singh pled guilty on Monday, June 17, and Ceraolo pled guilty on May 30.
The men gained access to the law enforcement portal by stealing the password of an officer’s account and using it to log in. The portal, maintained by an unnamed US federal law enforcement agency, was restricted to members of various law enforcement agencies to share intelligence from government databases with state and local officials. The site provided access to detailed nonpublic records involving narcotics and currency seizures and to law enforcement intelligence reports.

Enlarge (credit: Ric Tapia via Getty)
Hackers who stole terabytes of data from Ticketmaster and other customers of the cloud storage firm Snowflake claim they obtained access to some of the Snowflake accounts by first breaching a Belarusian-founded contractor that works with those customers.
About 165 customer accounts were potentially affected in the recent hacking campaign targeting Snowflake’s customers, but only a few of these have been identified so far. In addition to Ticketmaster, the banking firm Santander has also acknowledged that their data was stolen but declined to identify the account from which it was stolen. Wired, however, has independently confirmed that it was a Snowflake account; the stolen data included bank account details for 30 million customers, including 6 million account numbers and balances, 28 million credit card numbers, and human resources information about staff, according to a post published by the hackers. Lending Tree and Advance Auto Parts have also said they might be victims as well.
Snowflake has not revealed details about how the hackers accessed the accounts, saying only that the intruders did not directly breach Snowflake’s network. This week, Google-owned security firm Mandiant, one of the companies engaged by Snowflake to investigate the breaches, revealed in a blog post that in some cases the hackers first obtained access through third-party contractors, without identifying the contractors or stating how this access aided the hackers in breaching the Snowflake accounts.

Enlarge (credit: Getty Images)
Hardware manufacturer Asus has released updates patching multiple critical vulnerabilities that allow hackers to remotely take control of a range of router models with no authentication or interaction required of end users.
The most critical vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-3080 is an authentication bypass flaw that can allow remote attackers to log into a device without authentication. The vulnerability, according to the Taiwan Computer Emergency Response Team / Coordination Center (TWCERT/CC), carries a severity rating of 9.8 out of 10. Asus said the vulnerability affects the following routers:
A second vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-3079 affects the same router models. It stems from a buffer overflow flaw and allows remote hackers who have already obtained administrative access to an affected router to execute commands.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.
Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Enlarge (credit: Getty Images)
Ransomware criminals have quickly weaponized an easy-to-exploit vulnerability in the PHP programming language that executes malicious code on web servers, security researchers said.
As of Thursday, Internet scans performed by security firm Censys had detected 1,000 servers infected by a ransomware strain known as TellYouThePass, down from 1,800 detected on Monday. The servers, primarily located in China, no longer display their usual content; instead, many list the site’s file directory, which shows all files have been given a .locked extension, indicating they have been encrypted. An accompanying ransom note demands roughly $6,500 in exchange for the decryption key.
The output of PHP servers infected by TellYouThePass ransomware. (credit: Censys)

The accompanying ransom note. (credit: Censys)
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-4577 and carrying a severity rating of 9.8 out of 10, stems from errors in the way PHP converts Unicode characters into ASCII. A feature built into Windows known as Best Fit allows attackers to use a technique known as argument injection to convert user-supplied input into characters that pass malicious commands to the main PHP application. Exploits allow attackers to bypass CVE-2012-1823, a critical code execution vulnerability patched in PHP in 2012.
Google’s own Project Zero security research effort, which often finds and publishes vulnerabilities in both other companies’ and its own products, set its sights on Android once more, this time focusing on third-party kernel drivers.
Android’s open-source ecosystem has led to an incredible diversity of manufacturers and vendors developing software that runs on a broad variety of hardware. This hardware requires supporting drivers, meaning that many different codebases carry the potential to compromise a significant segment of Android phones. There are recent public examples of third-party drivers containing serious vulnerabilities that are exploited on Android. While there exists a well-established body of public (and In-the-Wild) security research on Android GPU drivers, other chipset components may not be as frequently audited so this research sought to explore those drivers in greater detail.
↫ Seth Jenkins
They found a whole host of security issues in these third-party kernel drivers in phones both from Google itself as well as from other companies. An interesting point the authors make is that because it’s getting ever harder to find 0-days in core Android, people with nefarious intent are looking at other parts of an Android system now, and these kernel drivers are an inviting avenue for them. They seem to focus mostly on GPU drivers, for now, but it stands to reason they’ll be targeting other drivers, too.
As usual with Android, the discovered exploits were often fixed, but the patches took way, way too long to find their way to end users due to the OEMs lagging behind when it comes to sending those patches to users. The authors propose wider adoption of Android APEX to make it easier to OEMs to deliver kernel patches to users faster.
I always like the Project Zero studies and articles, because they really take no prisoners, and whether they’re investigating someone else like Microsoft or Apple, or their own company Google, they go in hard, do not surgarcoat their findings, and apply the same standards to everyone.
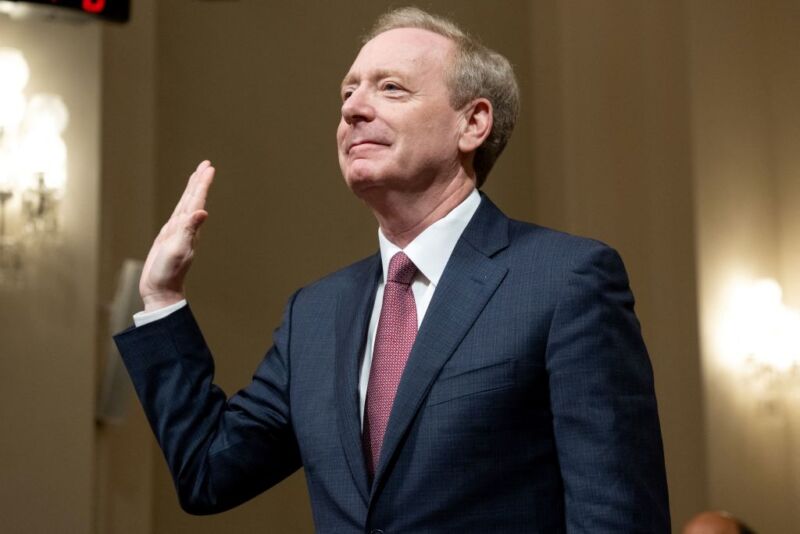

Enlarge / Brad Smith, vice chairman and president of Microsoft, is sworn in before testifying about Microsoft's cybersecurity work during a House Committee on Homeland Security hearing on Capitol Hill in Washington, DC, on June 13, 2024. (credit: SAUL LOEB / Contributor | AFP)
Microsoft is pivoting its company culture to make security a top priority, President Brad Smith testified to Congress on Thursday, promising that security will be "more important even than the company’s work on artificial intelligence."
Satya Nadella, Microsoft's CEO, "has taken on the responsibility personally to serve as the senior executive with overall accountability for Microsoft’s security," Smith told Congress.
His testimony comes after Microsoft admitted that it could have taken steps to prevent two aggressive nation-state cyberattacks from China and Russia.

© Eric Lee/The New York Times

© Eric Lee/The New York Times

Hackers working for the Chinese government gained access to more than 20,000 VPN appliances sold by Fortinet using a critical vulnerability that the company failed to disclose for two weeks after fixing it, Netherlands government officials said.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-42475, is a heap-based buffer overflow that allows hackers to remotely execute malicious code. It carries a severity rating of 9.8 out of 10. A maker of network security software, Fortinet silently fixed the vulnerability on November 28, 2022, but failed to mention the threat until December 12 of that year, when the company said it became aware of an “instance where this vulnerability was exploited in the wild.” On January 11, 2023—more than six weeks after the vulnerability was fixed—Fortinet warned a threat actor was exploiting it to infect government and government-related organizations with advanced custom-made malware.
The Netherlands officials first reported in February that Chinese state hackers had exploited CVE-2022-42475 to install an advanced and stealthy backdoor tracked as CoatHanger on Fortigate appliances inside the Dutch Ministry of Defense. Once installed, the never-before-seen malware, specifically designed for the underlying FortiOS operating system, was able to permanently reside on devices even when rebooted or receiving a firmware update. CoatHanger could also escape traditional detection measures, the officials warned. The damage resulting from the breach was limited, however, because infections were contained inside a segment reserved for non-classified uses.

Enlarge (credit: Just_Super via Getty)
Today, people around the world will head to school, doctor’s appointments, and pharmacies, only to be told, “Sorry, our computer systems are down.” The frequent culprit is a cybercrime gang operating on the other side of the world, demanding payment for system access or the safe return of stolen data.
The ransomware epidemic shows no signs of slowing down in 2024—despite increasing police crackdowns—and experts worry that it could soon enter a more violent phase.
“We’re definitely not winning the fight against ransomware right now,” Allan Liska, a threat intelligence analyst at Recorded Future, tells WIRED.

Enlarge (credit: Getty Images)
As many as 165 customers of cloud storage provider Snowflake have been compromised by a group that obtained login credentials through information-stealing malware, researchers said Monday.
On Friday, Lending Tree subsidiary QuoteWizard confirmed it was among the customers notified by Snowflake that it was affected in the incident. Lending Tree spokesperson Megan Greuling said the company is in the process of determining whether data stored on Snowflake has been stolen.
“That investigation is ongoing,” she wrote in an email. “As of this time, it does not appear that consumer financial account information was impacted, nor information of the parent entity, Lending Tree.”

Enlarge / Apple Senior VP of Software Engineering Craig Federighi announces "Private Cloud Compute" at WWDC 2024. (credit: Apple)
With most large language models being run on remote, cloud-based server farms, some users have been reluctant to share personally identifiable and/or private data with AI companies. In its WWDC keynote today, Apple stressed that the new "Apple Intelligence" system it's integrating into its products will use a new "Private Cloud Compute" to ensure any data processed on its cloud servers is protected in a transparent and verifiable way.
"You should not have to hand over all the details of your life to be warehoused and analyzed in someone's AI cloud," Apple Senior VP of Software Engineering Craig Federighi said.
Part of what Apple calls "a brand new standard for privacy and AI" is achieved through on-device processing. Federighi said "many" of Apple's generative AI models can run entirely on a device powered by an A17+ or M-series chips, eliminating the risk of sending your personal data to a remote server.

A critical vulnerability in the PHP programming language can be trivially exploited to execute malicious code on Windows devices, security researchers warned as they urged those affected to take action before the weekend starts.
Within 24 hours of the vulnerability and accompanying patch being published, researchers from the nonprofit security organization Shadowserver reported Internet scans designed to identify servers that are susceptible to attacks. That—combined with (1) the ease of exploitation, (2) the availability of proof-of-concept attack code, (3) the severity of remotely executing code on vulnerable machines, and (4) the widely used XAMPP platform being vulnerable by default—has prompted security practitioners to urge admins check to see if their PHP servers are affected before starting the weekend.
“A nasty bug with a very simple exploit—perfect for a Friday afternoon,” researchers with security firm WatchTowr wrote.

Enlarge (credit: Getty Images)
The FBI is urging victims of one of the most prolific ransomware groups to come forward after agents recovered thousands of decryption keys that may allow the recovery of data that has remained inaccessible for months or years.
The revelation, made Wednesday by a top FBI official, comes three months after an international roster of law enforcement agencies seized servers and other infrastructure used by LockBit, a ransomware syndicate that authorities say has extorted more than $1 billion from 7,000 victims around the world. Authorities said at the time that they took control of 1,000 decryption keys, 4,000 accounts, and 34 servers and froze 200 cryptocurrency accounts associated with the operation.
At a speech before a cybersecurity conference in Boston, FBI Cyber Assistant Director Bryan Vorndran said Wednesday that agents have also recovered an asset that will be of intense interest to thousands of LockBit victims—the decryption keys that could allow them to unlock data that’s been held for ransom by LockBit associates.

Enlarge / A visual from the fake documentary Olympics Has Fallen produced by Russia-affiliated influence actor Storm-1679. (credit: Microsoft)
Last year, a feature-length documentary purportedly produced by Netflix began circulating on Telegram. Titled “Olympics have Fallen” and narrated by a voice with a striking similarity to that of actor Tom Cruise, it sharply criticized the leadership of the International Olympic Committee. The slickly produced film, claiming five-star reviews from The New York Times, Washington Post, and BBC, was quickly amplified on social media. Among those seemingly endorsing the documentary were celebrities on the platform Cameo.
A recently published report by Microsoft (PDF) said the film was not a documentary, had received no such reviews, and that the narrator's voice was an AI-produced deep fake of Cruise. It also said the endorsements on Cameo were faked. The Microsoft Threat Intelligence Report went on to say that the fraudulent documentary and endorsements were only one of many elaborate hoaxes created by agents of the Russian government in a yearlong influence operation intended to discredit the International Olympic Committee (IOC) and deter participation and attendance at the Paris Olympics starting next month.
Other examples of the Kremlin’s ongoing influence operation include:

© Li Qiang for The New York Times

© An Rong Xu for The New York Times

© Stephen Speranza for The New York Times

© Dia Dipasupil/Getty Images
William Brown, developer of webauthn-rs, has written a scathing blog post detailing how corporate interests – namely, Apple and Google – have completely and utterly destroyed the concept of passkeys. The basic gist is that Apple and Google were more interested in control and locking in users than in providing a user-friendly passwordless future, and in doing so have made passkeys effectively a worse user experience than just using passwords in a password manager.
Since then Passkeys are now seen as a way to capture users and audiences into a platform. What better way to encourage long term entrapment of users then by locking all their credentials into your platform, and even better, credentials that can’t be extracted or exported in any capacity.
Both Chrome and Safari will try to force you into using either hybrid (caBLE) where you scan a QR code with your phone to authenticate – you have to click through menus to use a security key. caBLE is not even a good experience, taking more than 60 seconds work in most cases. The UI is beyond obnoxious at this point. Sometimes I think the password game has a better ux.
The more egregious offender is Android, which won’t even activate your security key if the website sends the set of options that are needed for Passkeys. This means the IDP gets to choose what device you enroll without your input. And of course, all the developer examples only show you the options to activate “Google Passkeys stored in Google Password Manager”. After all, why would you want to use anything else?
↫ William Brown
The whole post is a sobering read of how a dream of passwordless, and even usernameless, authentication was right within our grasp, usable by everyone, until Apple and Google got involved and enshittified the standards and tools to promote lock-in and their own interests above the user experience. If even someone as knowledgeable about this subject as Brown, who writes actual software to make these things work, is advising against using passkeys, you know something’s gone horribly wrong.
I also looked into possibly using passkeys, including using things like a Yubikey, but the process seems so complex and unpleasant that I, too, concluded just sticking to Bitwarden and my favourite open source TFA application was a far superior user experience.

© Jessica Hill/Associated Press