Apple AirPods Bug Allows Eavesdropping



A Chinese cyberespionage group and two more possibly from China and North Korea are using ransomware in their attacks to either add financial gains to their efforts or to cover their tracks by convincing victims and cybersecurity experts that the intrusions were something other than spy campaigns. Researchers with SentinelOne have been tracking two clusters..
The post Chinese APT Groups Use Ransomware to Hide Spying Activities appeared first on Security Boulevard.
The CIS Controls list hardware asset management as the most important security control, but how many organizations keep track of the components that make up the servers in their datacenter? Components such as baseboard management controllers, UEFI firmware, SSDs, CPUs, TPMs, and network cards are incredibly complex with their own sub-components.
The post Protecting the Soft Underbelly of the Data Center appeared first on Eclypsium | Supply Chain Security for the Modern Enterprise.
The post Protecting the Soft Underbelly of the Data Center appeared first on Security Boulevard.

WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange returned to Australia, hours after pleading guilty to obtaining and publishing U.S. military secrets.
The post WikiLeaks Founder Julian Assange Returns to Australia a Free Man After US Legal Battle Ends appeared first on SecurityWeek.

Recent reporting highlighted new techniques for a prominent group that already possessed a deep set of capabilities. As the pace of adversary TTP evolution increases, organizations must stay vigilant and regularly reassess their defenses against the latest TTPs used by relevant threats. This holds true even amid reports of threat group disruptions, as many groups continue to demonstrate resilience in the face of law enforcement operations and other pressures.
The post Scattered Spider: Evolving & Resilient Group Proves Need for Constant Defender Vigilance appeared first on Security Boulevard.
Google has announced new Chrome Enterprise Core features that should be very useful to IT and security teams.
The post Google Unveils New Chrome Enterprise Core Features for IT, Security Teams appeared first on SecurityWeek.
The post Pen Testing Across the Environment: External, Internal, and Wireless Assessments appeared first on Digital Defense.
The post Pen Testing Across the Environment: External, Internal, and Wireless Assessments appeared first on Security Boulevard.
It’s easy to confuse CSPM and SSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management and SaaS Security Posture Management). They both secure assets on the cloud, automatically identify misconfigurations, and detect identity-based threats. The difference between the two lies in the areas that they protect. SSPMs secure SaaS applications, while CSPMs secure cloud services, such as AWS or […]
The post A WIN for Cloud Security with Adaptive Shield and Wiz appeared first on Adaptive Shield.
The post A WIN for Cloud Security with Adaptive Shield and Wiz appeared first on Security Boulevard.
ReversingLabs researchers have made it a priority to monitor public, open source repositories for malicious packages that may lurk on them in recent years. The number and frequency of malicious packages has increased steadily as malicious actors turn to software supply chains for an easy route into hundreds, thousands or even tens of thousands of protected IT environments.
Many of the packages the RL threat research team has found are what we term “infostealers” — malicious software that is designed to grab sensitive information. For example, our team recently wrote about a package discovered on the NuGet repository, SqzrFramework480.dll, that contained features for capturing a screenshot, sending ping packets, as well as opening a socket and sending data over it. The package contained information — including a graphic — that suggested it was targeting BOZHON Precision Industry Technology Co., a China-based firm that does industrial and digital equipment manufacturing.
RL researchers frequently discover downloaders and malicious applications designed to fetch other software — so called second (or third) “stages” that are often open source "infostealers" or simple “beacon-backs” that red team operators use to plant a flag within target environments to prove they were successful in breaching defenses.
Whatever their purpose, all of the packages we detect as malicious are reported to the relevant maintainers of the affected repositories. In our team's experience, they are removed shortly after. That’s good for developers and development teams, as it removes potentially damaging code from public repositories where it might find its way onto developers’ systems, or even integrated into legitimate applications and services.
But there’s a problem with this approach: The sheer scale of the open source ecosystem is so large that it is impossible for any single group of researchers to keep abreast of and police massive repositories like Python Package Index (PyPI), npm, NuGet, VS Code Marketplace and others. On any given day, RL researchers, using RL Spectra Assure platform, identify dozens of malicious packages spread across these repositories, but far more packages may lurk undetected — suspicious but not overtly malicious.
The post Malicious npm package targets AWS users appeared first on Security Boulevard.
Spotting compromises hidden deep in open source- or commercial supply chains is difficult under the best of circumstances. For developers and development teams tasked with achieving aggressive development and release goals — an environment in which software security and integrity are low priorities — the job is even harder. That’s why, today, ReversingLabs introduced a new offering that helps developers to rapidly assess the security and quality of millions of open source packages spread across platforms such as npm, PyPI and RubyGems.
Spectra Assure Community is a tool that enables developers, product security teams, and release managers to scan open source components to identify the best building blocks for their products. Using Spectra’s unique combination of advanced threat detection, comprehensive analysis, and standardized assessments, it helps developers determine whether packages that they wish to use are free from malicious code and supply chain attacks.
The post New Portal Helps Devs Spot Malicious Open Source Packages appeared first on Security Boulevard.

The Rapid7 Take Command summit unveiled crucial findings from the 2024 Attack Intelligence Report, offering invaluable insights for cybersecurity professionals navigating today's complex threat landscape.
"Our research shows that more than 40% of incident responses in 2023 stemmed from remote remote access exploits without multifactor authentication. Basic security components are still crucial in making attacks harder." - Caitlin Condon, Director Vulnerability Intelligence, Rapid7
The 2024 Attack Intelligence Report provides deep insights into the evolving threat landscape, highlighting the rise of zero-day exploits, the critical vulnerabilities in network edge technologies, and the rampant increase in ransomware incidents, you can view it here.
For a deeper dive into these findings, click through to watch the full video and stay ahead of attackers.
EFF is excited to kick off a new series of livestream events this summer! Please join EFF staff and fellow digital freedom supporters as we dive into three topics near and dear to our hearts.
In the first segment of EFF's livestream series, we'll dive into the impact of the U.S. Supreme Court's recent opinions on technology and civil liberties. Get an expert's look at the court cases making the biggest waves for tech users with our panel featuring EFF Civil Liberties Director David Greene.
This summer marks the two-year anniversary of the Dobbs decision overturning Roe vs Wade. Join EFF for a livestream discussion about restrictions to reproductive healthcare and the choices women must face in the digital age where everything is connected, and surveillance is rampant. Learn what’s happening across the United States and how you can get involved.
Do you know what to do if you’re subjected to a search or arrest at a protest? Join EFF for a livestream discussion about how to protect your electronic devices and digital assets before, during, and after a demonstration. Learn how you can avoid confiscation or forced deletion of media, and keep your movements and associations private.
We hope you can join for all three events! Be sure to share this post with any interested friends and tell them to join us! Thank you for helping EFF spread the word about privacy and free expression online.
We encourage everyone to join us live for these discussions. Please note that they will be recorded. Recordings will be available following each event.


 By combining their resources and expertise, the CPPA and CNIL aim to tackle a range of data privacy issues, from the implications of new technologies to the enforcement of data protection laws. This partnership is expected to lead to the development of innovative solutions and best practices that can be shared with other regulatory bodies around the world.
As more organizations and governments recognize the importance of safeguarding personal data, the need for robust and cooperative frameworks becomes increasingly clear. The CPPA-CNIL partnership serves as a model for other regions looking to strengthen their data privacy measures through international collaboration.
By combining their resources and expertise, the CPPA and CNIL aim to tackle a range of data privacy issues, from the implications of new technologies to the enforcement of data protection laws. This partnership is expected to lead to the development of innovative solutions and best practices that can be shared with other regulatory bodies around the world.
As more organizations and governments recognize the importance of safeguarding personal data, the need for robust and cooperative frameworks becomes increasingly clear. The CPPA-CNIL partnership serves as a model for other regions looking to strengthen their data privacy measures through international collaboration. 
 Source: X[/caption]
The breached data purportedly includes names of employees, 6,623 unique email addresses, their codes, date of birth, gender, policy name, relationships, dates of joining, effective dates, statuses, and entities.
To substantiate the claim, the threat actor 888 provided a sample of the data breach, which contains details of Credit Suisse employees in India.
[caption id="attachment_79025" align="alignnone" width="1362"]
Source: X[/caption]
The breached data purportedly includes names of employees, 6,623 unique email addresses, their codes, date of birth, gender, policy name, relationships, dates of joining, effective dates, statuses, and entities.
To substantiate the claim, the threat actor 888 provided a sample of the data breach, which contains details of Credit Suisse employees in India.
[caption id="attachment_79025" align="alignnone" width="1362"] Source: X[/caption]
The TA, however, did not provide a specific price for the sale of data and has requested potential buyers to quote a figure. The hacker commented that they are only accepting cryptocurrency as the mode of payment. More specifically, the hacker was open to payment on Monero (XMR), a digital currency renowned for its privacy and anonymity attributes. This method of payment is often utilized in illegal transactions to evade detection.
Despite these claims by the threat actor, a closer inspection reveals that the bank’s website is currently functioning normally, showing no signs of a security breach. The Cyber Express has reached out to the bank to verify the alleged cyberattack. As of now, no official statements or responses have been received, leaving the claims unverified.
Source: X[/caption]
The TA, however, did not provide a specific price for the sale of data and has requested potential buyers to quote a figure. The hacker commented that they are only accepting cryptocurrency as the mode of payment. More specifically, the hacker was open to payment on Monero (XMR), a digital currency renowned for its privacy and anonymity attributes. This method of payment is often utilized in illegal transactions to evade detection.
Despite these claims by the threat actor, a closer inspection reveals that the bank’s website is currently functioning normally, showing no signs of a security breach. The Cyber Express has reached out to the bank to verify the alleged cyberattack. As of now, no official statements or responses have been received, leaving the claims unverified.
On June 23rd, LockBit announced breaching the US Federal Reserve System, while security experts remained skeptical. The Russian threat group claimed to exfiltrate 33 terabytes of banking information from the USA’s central bank servers. They also threatened to publish the data in the following 48 hours unless the victims would pay ransom. Source – Cybernews.com […]
The post LockBit Claims Breaching the US Federal Reserve but Fails to Prove It appeared first on Heimdal Security Blog.
A shockwave went through the financial world when ransomware group LockBit claimed to have breached the US Federal Reserve, the central banking system of the United States.
On LockBit’s dark web leak site, the group threatened to release over 30 TB of banking information containing Americans’ banking data if a ransom wasn’t paid by June 25:

“Federal banking is the term for the way the Federal Bank of America distributes its money. The Reserve operates twelve banking districts around the country which oversee money distribution within their respective districts. The twelve cities which are home to the Reserve Banks are Boston, New York City, Philadelphia, Richmond, Atlanta, Dallas, Saint Louis, Cleveland, Chicago, Minneapolis, Kansas City and San Francisco.
33 terabytes of juicy banking information containing American’s banking secrets.”
The statement ends expressing the group’s disappointment about a negotiator who apparently offered to pay $50,000.
So, you can imagine that everyone was anticipating the end of the countdown that signalled the release of the stolen data with bated breath.
However, when that deadline passed and the data was released, people who looked at the data found it did not, in fact, belong to the Federal Reserve but instead to a particular financial organization: Evolve Bank & Trust.

All the links lead to directories containing data that seems to belong to Evolve.
There hasn’t been enough time to do a full analysis of the huge amount of data, but it appears it is only remotely tied to the Federal Reserve by some included links to a Federal Reserve press link from mid-June.
At that time, the US Federal Reserve Board penalized Evolve Bancorp and its subsidiary, Evolve Bank & Trust, for multiple “deficiencies” in the bank’s risk management, anti-money laundering (AML) and compliance practices.
According to the Federal Reserve statement released at the time:
“In addition, Evolve did not maintain an effective risk management program or controls sufficient to comply with anti-money laundering laws and laws protecting consumers.”
So, as expected, LockBit drew a lot of attention under false pretences.
The group was disrupted by law enforcement in February of 2024 and their activity diminished as a result. As the ThreatDown monthly ransomware review of May review pointed out:
“While LockBit is technically still alive, it’s fair to say the group is not what it was: Not only are its attacks dwindling, but in early May law enforcement also revealed the identity of alleged LockBit leader Dmitry Khoroshev, aka LockBitSupp. LockBitSupp, who is now subjected to a series of asset freezes and travel bans, also has a reward of up to $10 million over his head for information that leads to his arrest.”
And recently the FBI announced it had over 7,000 LockBit decryption keys in its possession, allowing it to help victims to recover data encrypted by the gang in past attacks. LockBit ransomware has impacted over 1,800 US victims, according to FBI stats.
Back to the data, it’s good news it appears not to be from the Federal Reserve. However, it’s not good news for customers of Evolve Bank & Trust and their data may well have been stolen and published. And it’s a lot of data.
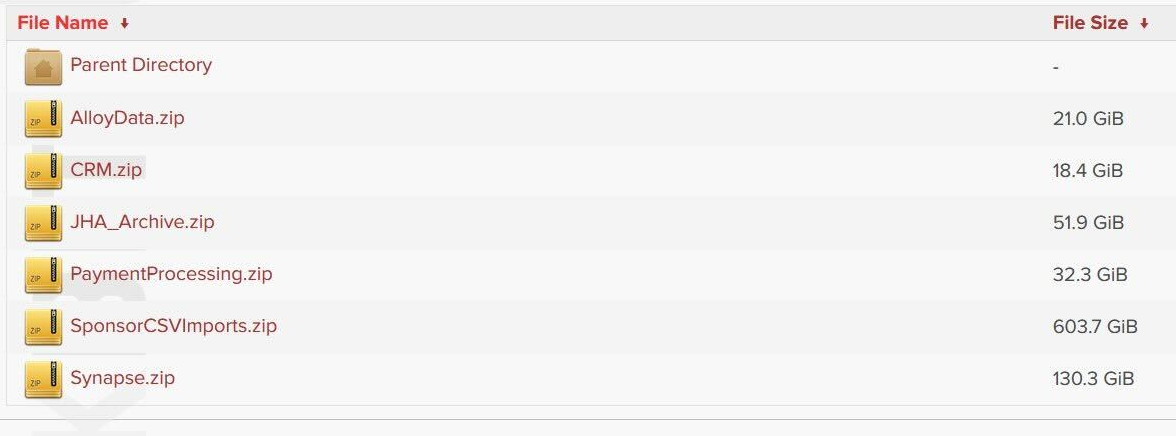
We’ll keep you updated on this developing story. For now, there’s no official statement from Evolve, but there are general things to know if you think you have been involved in a data breach.
There are some actions you can take if you are, or suspect you may have been, the victim of a data breach.
Malwarebytes has a new free tool for you to check how much of your personal data has been exposed online. Submit your email address (it’s best to give the one you most frequently use) to our free Digital Footprint scan and we’ll give you a report and recommendations.
We don’t just report on threats – we help safeguard your entire digital identity
Cybersecurity risks should never spread beyond a headline. Protect your—and your family’s—personal information by using identity protection.
New GrimResource technique exploits a 2018-old, unpatched, Windows XSS flaw and crafted MSC files to deploy malware via the Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Researchers detected the new exploitation technique in the wild on June 6th, 2024. Exploiting the Microsoft Management Console could enable hackers to evade security measures and gain initial access. Although researchers reported […]
The post GrimResource Technique Exploits Years-Old Unpatched Windows XSS Flaw appeared first on Heimdal Security Blog.

 Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The dashboard boasts several essential features designed to streamline the ransomware deployment process. Users can track the success of their campaigns with detailed statistics, manage communications via an integrated chat function, and customize ransomware configurations using the built-in builder tool.
In addition to its current capabilities, KillSec has announced forthcoming enhancements to its RaaS program. These include a stresser tool for launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, automated phone call capabilities to pressure victims into paying ransoms, and an advanced stealer for harvesting sensitive data such as passwords and financial information.
Access to KillSec's RaaS program is available for a fee of $250, aimed at "trusted individuals," with KillSec taking a 12% commission from any ransom payments collected. This pricing model highlights the group's commitment to making advanced cyber weaponry accessible while maintaining a profitable partnership with their clients.
Source: Dark Web[/caption]
The dashboard boasts several essential features designed to streamline the ransomware deployment process. Users can track the success of their campaigns with detailed statistics, manage communications via an integrated chat function, and customize ransomware configurations using the built-in builder tool.
In addition to its current capabilities, KillSec has announced forthcoming enhancements to its RaaS program. These include a stresser tool for launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, automated phone call capabilities to pressure victims into paying ransoms, and an advanced stealer for harvesting sensitive data such as passwords and financial information.
Access to KillSec's RaaS program is available for a fee of $250, aimed at "trusted individuals," with KillSec taking a 12% commission from any ransom payments collected. This pricing model highlights the group's commitment to making advanced cyber weaponry accessible while maintaining a profitable partnership with their clients.
Choosing an IT management software is one of the most important decisions you make as an IT team. There are a few well-known platforms on the market, one being NinjaOne. Considering the feedback from review sites, NinjaOne customers are switching to alternatives mainly because of a poor user experience, slow customer support, complex configuration, and […]
The post Top 10 NinjaOne Alternatives to Consider in 2024 appeared first on Heimdal Security Blog.


30,000 websites at risk: Check yours ASAP! (800 Million Ostriches Can’t Be Wrong.)
The post WordPress Plugin Supply Chain Attack Gets Worse appeared first on Security Boulevard.

A report from the Government Accountability Office (GAO) highlighted an urgent need to address critical cybersecurity challenges facing the nation.
The post GAO Urges Action to Address Critical Cybersecurity Challenges Facing U.S. appeared first on Security Boulevard.

In the first quarter of 2024, nearly half of all security incidents our team responded to involved multi-factor authentication (MFA) issues, according to the latest Cisco Talos report.
The post Misconfigured MFA Increasingly Targeted by Cybercriminals appeared first on Security Boulevard.
Google has disrupted over 175,000 YouTube and Blogger instances related to the Chinese influence operation Dragonbridge.
The post Google Disrupts More China-Linked Dragonbridge Influence Operations appeared first on SecurityWeek.
_Kjetil_Kolbj%C3%B8rnsrud_Alamy.jpg)
The post The Check Point Challenge: Safeguarding Against the Latest CVE appeared first on Votiro.
The post The Check Point Challenge: Safeguarding Against the Latest CVE appeared first on Security Boulevard.
_Frank_Herholdt_alamy.jpg)
Organizations face an overwhelming number of vulnerabilities and threats. The traditional approach has been to prioritize exposures—identifying and addressing the most critical vulnerabilities first. However, this method, while logical on the surface, has significant limitations. At Veriti, we advocate for a different strategy: prioritizing actions. By focusing on remediations rather than merely cataloging exposures, we believe […]
The post Prioritizing Exposures vs. Prioritizing Actions appeared first on VERITI.
The post Prioritizing Exposures vs. Prioritizing Actions appeared first on Security Boulevard.
Freed from the shackles of always demanding a technical background, the CISO can concentrate on building a diverse team comprising multiple skills.
The post Gaining and Retaining Security Talent: A Cheat Sheet for CISOs appeared first on SecurityWeek.
Some expressed concern about a rise in hybrid attacks by Russia – including allegations of election interference, cyberattacks and sabotage.
The post The EU Targets Russia’s LNG Ghost Fleet With Sanctions as Concern Mounts About Hybrid Attacks appeared first on SecurityWeek.
Today, CISA, in partnership with the Federal Bureau of Investigation, Australian Signals Directorate’s Australian Cyber Security Centre, and Canadian Cyber Security Center, released Exploring Memory Safety in Critical Open Source Projects. This guidance was crafted to provide organizations with findings on the scale of memory safety risk in selected open source software (OSS).
This joint guidance builds on the guide The Case for Memory Safe Roadmaps by providing a starting point for software manufacturers to create memory safe roadmaps, including plans to address memory safety in external dependencies which commonly include OSS. Exploring Memory Safety in Critical Open Source Projects also aligns with the 2023 National Cybersecurity Strategy and corresponding implementation plan, which discusses investing in memory safety and collaborating with the open source community—including the establishment of the interagency Open Source Software Security Initiative (OS3I) and investment in memory-safe programming languages.
CISA encourages all organizations and software manufacturers to review the methodology and results found in the guidance to:
To learn more about taking a top-down approach to developing secure products, visit CISA’s Secure by Design webpage.
CISA has added three new vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog, based on evidence of active exploitation.
These types of vulnerabilities are frequent attack vectors for malicious cyber actors and pose significant risks to the federal enterprise.
Binding Operational Directive (BOD) 22-01: Reducing the Significant Risk of Known Exploited Vulnerabilities established the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog as a living list of known Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) that carry significant risk to the federal enterprise. BOD 22-01 requires Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies to remediate identified vulnerabilities by the due date to protect FCEB networks against active threats. See the BOD 22-01 Fact Sheet for more information.
Although BOD 22-01 only applies to FCEB agencies, CISA strongly urges all organizations to reduce their exposure to cyberattacks by prioritizing timely remediation of Catalog vulnerabilities as part of their vulnerability management practice. CISA will continue to add vulnerabilities to the catalog that meet the specified criteria.
The P2Pinfect worm targeting Redis servers has been updated with ransomware and cryptocurrency mining payloads.
The post P2Pinfect Worm Now Dropping Ransomware on Redis Servers appeared first on SecurityWeek.
Rate limiting is a well-known technique for limiting network traffic to web servers, APIs, or other online services. It is also one of the methods available to you for blocking DDoS attackers from flooding your system with requests and exhausting network capacity, storage, and memory. You typically define rate-limiting rules in your Web Application Firewall […]
The post 6 Tips for Preventing DDoS Attacks Using Rate Limits appeared first on Security Boulevard.
The tragedy of the commons is a concept in economics and ecology that describes a situation where individuals, acting in their own self-interest, collectively deplete a shared resource. In simpler terms, it's the idea that when a resource is available to everyone without restriction, some individuals tend to overuse it, leading to its eventual depletion and harming everyone in the long run. In the case of Maven Central, we are experiencing an unwitting tyranny by the few.
The post Maven Central and the tragedy of the commons appeared first on Security Boulevard.
More than 100,000 websites are affected by a supply chain attack injecting malware via a Polyfill domain.
The post Polyfill Supply Chain Attack Hits Over 100k Websites appeared first on SecurityWeek.
Multiple vulnerabilities have been addressed in ADOdb, a PHP database abstraction layer library. These vulnerabilities could cause severe security issues, such as SQL injection attacks, cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, and authentication bypasses. The Ubuntu security team has released updates to address them in various versions of Ubuntu, including Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, Ubuntu […]
The post Critical ADOdb Vulnerabilities Fixed in Ubuntu appeared first on TuxCare.
The post Critical ADOdb Vulnerabilities Fixed in Ubuntu appeared first on Security Boulevard.
Containerized applications offer several advantages over traditional deployment methods, making them a powerful tool for modern application development and deployment. Understanding the security complexities of containers and implementing targeted security measures is crucial for organizations to protect their applications and data. Adopting specialized security practices, such as Linux live kernel patching, is essential in maintaining […]
The post Navigating Security Challenges in Containerized Applications appeared first on TuxCare.
The post Navigating Security Challenges in Containerized Applications appeared first on Security Boulevard.

 Source: X[/caption]
The threat actor claims to have accessed 1.2 TB of organization data, including accounting, budget, and financial data; contract data and NDAs; files from the CFO's computer; operational and business files; and email and PST archives. The group has also disclosed sensitive information such as the names, personal email addresses, and phone numbers of BBB’s CEO, vice president, chief accreditation officer, and chief activation officer.
The other organization that has allegedly fallen victim to the ransomware group is US Dermatology Partners. The organization, with a revenue of $213.7 Million, is one of the premier dermatology practitioners in the USA, caring for over two million patients annually.
[caption id="attachment_79002" align="alignnone" width="1259"]
Source: X[/caption]
The threat actor claims to have accessed 1.2 TB of organization data, including accounting, budget, and financial data; contract data and NDAs; files from the CFO's computer; operational and business files; and email and PST archives. The group has also disclosed sensitive information such as the names, personal email addresses, and phone numbers of BBB’s CEO, vice president, chief accreditation officer, and chief activation officer.
The other organization that has allegedly fallen victim to the ransomware group is US Dermatology Partners. The organization, with a revenue of $213.7 Million, is one of the premier dermatology practitioners in the USA, caring for over two million patients annually.
[caption id="attachment_79002" align="alignnone" width="1259"] Source: X[/caption]
The hackers claimed to have accessed 300 GB of organization data, including personal data, accounting and budget information, financial data, contract data and NDAs, and employee profiles.
Source: X[/caption]
The hackers claimed to have accessed 300 GB of organization data, including personal data, accounting and budget information, financial data, contract data and NDAs, and employee profiles.

Source: www.databreachtoday.com – Author: 1 Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning , Cyberwarfare / Nation-State Attacks , Fraud Management & Cybercrime New Report Urges Public-Private Collaboration to Reduce Chemical, Nuclear AI Risks Chris Riotta (@chrisriotta) • June 25, 2024 The U.S. federal government warned that artificial intelligence lowers the barriers to conceptualizing and conducting […]
La entrada US DHS Warns of AI-Fueled Chemical and Biological Threats – Source: www.databreachtoday.com se publicó primero en CISO2CISO.COM & CYBER SECURITY GROUP.

Source: www.databreachtoday.com – Author: 1 Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning , Governance & Risk Management , Next-Generation Technologies & Secure Development Companies Eager for Tools Are Putting AI’s Transformative Power Ahead of Security Rashmi Ramesh (rashmiramesh_) • June 25, 2024 Oh, no – not all Ollama administrators have patched against the “Probllama” flaw. […]
La entrada Patched Weeks Ago, RCE Bug in AI Tool Still a ‘Probllama’ – Source: www.databreachtoday.com se publicó primero en CISO2CISO.COM & CYBER SECURITY GROUP.

Source: www.databreachtoday.com – Author: 1 Healthcare , Industry Specific , Standards, Regulations & Compliance John Riggi of the American Hospital Association on HHS’ Upcoming Cyber Regulations Marianne Kolbasuk McGee (HealthInfoSec) • June 25, 2024 John Riggi, national cybersecurity and risk adviser, American Hospital Association White House efforts to ratchet up healthcare sector cybersecurity […]
La entrada Why New Cyber Penalties May Strain Hospital Resources – Source: www.databreachtoday.com se publicó primero en CISO2CISO.COM & CYBER SECURITY GROUP.