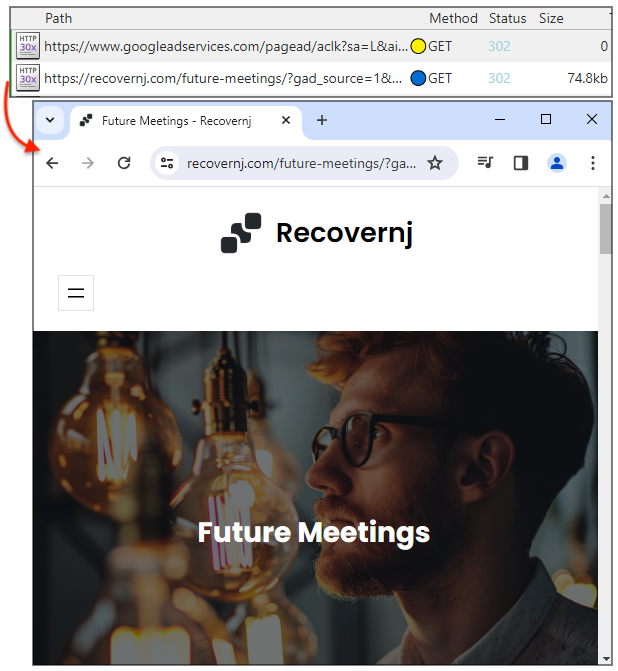
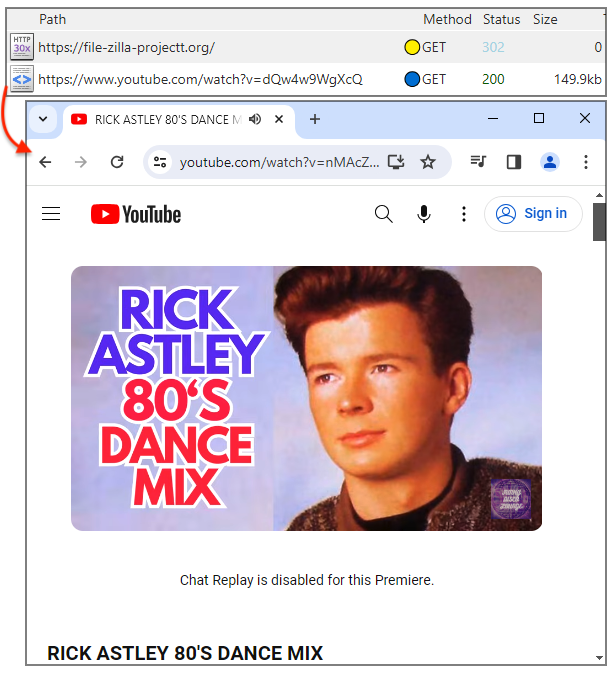
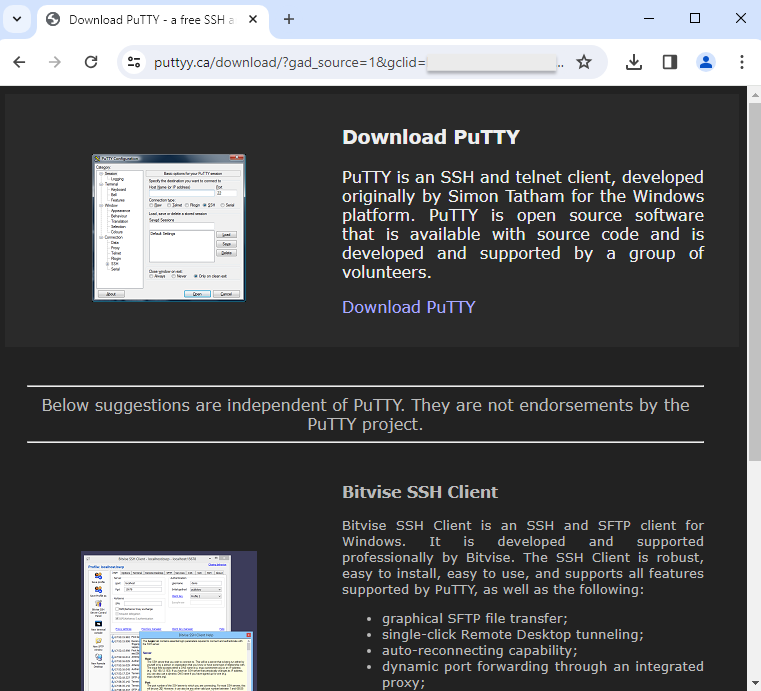
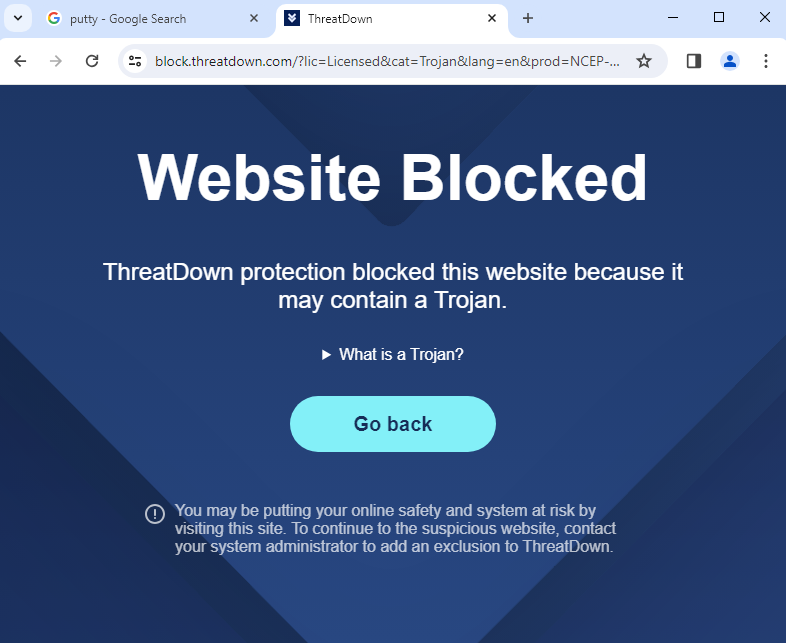
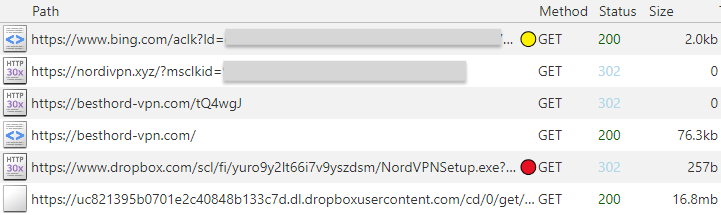
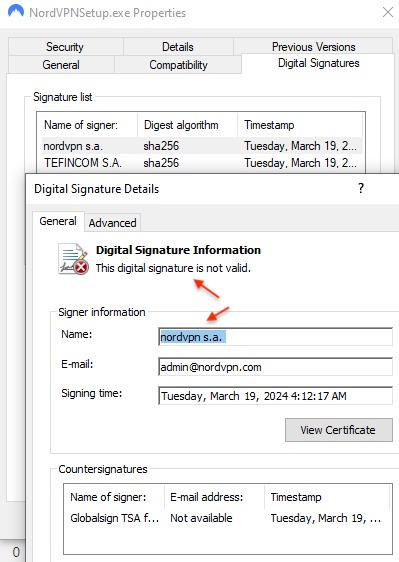
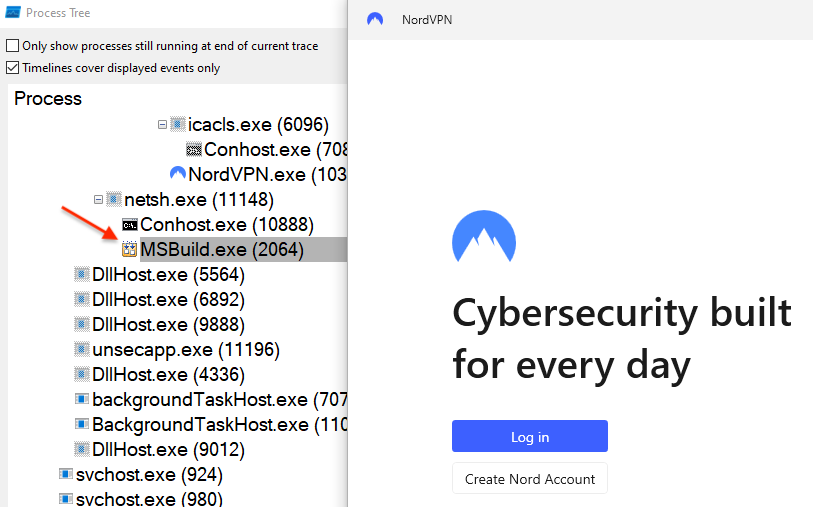
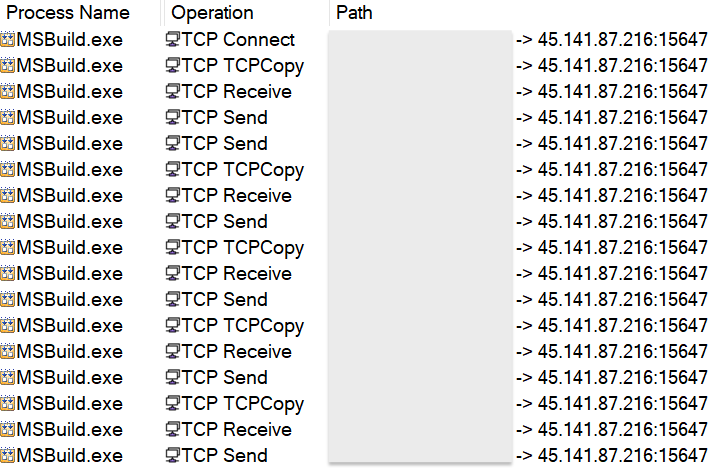
Researchers from Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL) have
discovered a QR code-based phishing campaign that uses malicious Word documents masquerading as official documents from the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of China. Users are tricked into providing bank card details and passwords under the guise of identity verification and authentication processes.
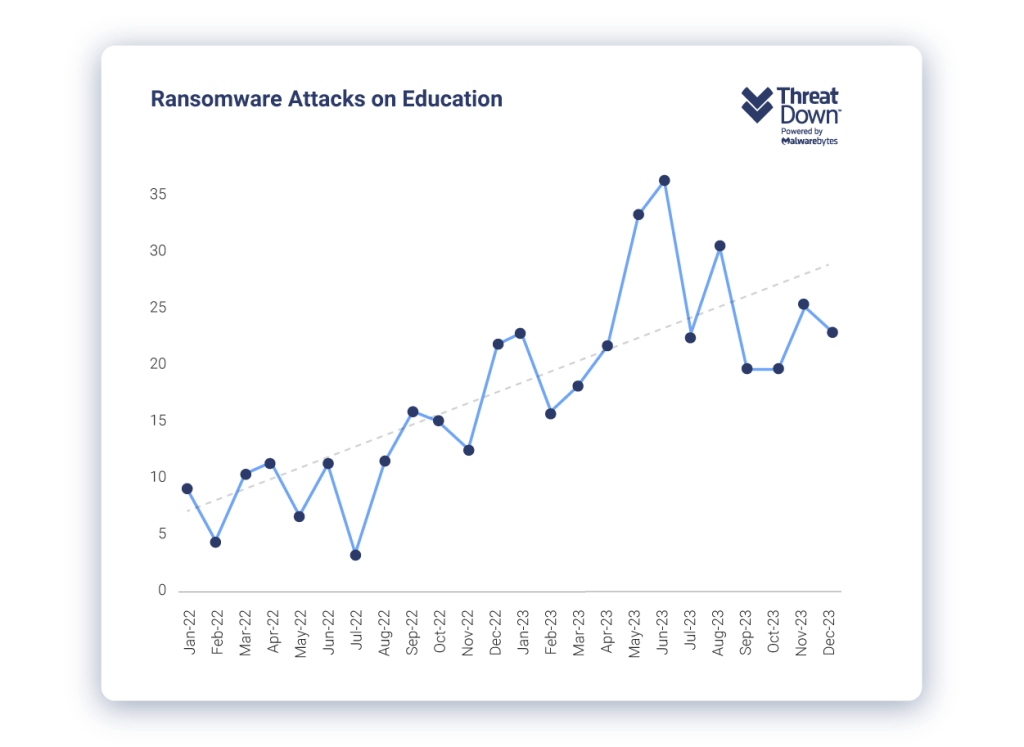
QR Code-Based Phishing Campaign
QR code phishing attacks have escalated significantly this year, with cybercriminals leveraging this technology to steal personal and financial information. Threat actors (TAs) are embedding QR codes in office documents and redirecting users to fraudulent websites designed to harvest sensitive
data.
In the ever-evolving
cyber threat landscape, a new vector has emerged: QR code-based phishing campaign. Cybercriminals are increasingly embedding QR codes in malicious documents, which when scanned direct users to fraudulent websites. This tactic has seen a marked rise in 2024 following a trend that started during the COVID-19 pandemic, when QR codes became widely adopted for contactless transactions and information sharing.
The
Hoxhunt Challenge highlighted a 22% increase in QR code phishing during late 2023, and research by Abnormal Security
indicates that 89.3% of these attacks aim to steal credentials.
The growing familiarity with QR codes has created a false sense of
security, making it easier for cybercriminals to exploit them. QR codes can mask destination URLs, preventing users from easily verifying the legitimacy of the site they are being redirected to.
Recent QR Code Campaigns and Techniques
Recently, Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs uncovered a sophisticated phishing
campaign targeting individuals in China. This campaign saw the use of Microsoft Word documents embedded with QR codes, which are distributed via spam email attachments. The documents were designed to appear as official notices from the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of China, offering labor subsidies above 1000 RMB to lure victims.
[caption id="attachment_77666" align="aligncenter" width="769"]

MS Word file containing QR code (Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The documents are meticulously crafted to look authentic, complete with official logos and language that mimics government communications. Once the QR code in the
document is scanned, it redirects the user to a phishing site designed to collect sensitive information.
This particular campaign stands out due to its use of a Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA), which generates a series of seemingly random domain names. DGA is a program that generates large numbers of new domain names. Cybercriminals and botnet operators generally use it to frequently change the domains used to launch
malware attacks. This technique enables hackers to avoid malware-detection solutions that block specific domain names and static IP addresses.
The latest campaign isn't an isolated incident. A similar phishing operation was documented in January 2023 by Fortinet, where cybercriminals impersonated another Chinese government agency. This resurgence in QR code phishing attacks indicates a persistent threat targeting Chinese citizens, with malicious actors continually refining their tactics to evade detection.
The QR Code Phishing Process
The phishing process begins with the user scanning the QR code from the malicious Word document. This action takes them to the phishing site, which initially displays a dialogue box promising a labor subsidy. The site is designed to appear official, complete with government logos and formal language to enhance credibility.
The phishing site instructs the user to provide personal information, starting with their name and national ID. This step is presented as a necessary part of the application process for the subsidy. Once the user enters this information, they are directed to a second page that requests detailed bank card information, including the card number, phone number, and balance. This information is ostensibly required for identity verification and to process the subsidy.
After collecting the bank card details, the phishing site asks the user to wait while their information is "verified." This waiting period is a tactic used to add a sense of legitimacy to the process. Following this, the site prompts the user to enter their bank card password, under the guise of further verification.
This password is suspected to be the same as the payment password used for domestic credit card transactions. By obtaining this password along with the card details, the threat actors can perform unauthorized transactions, leading to significant financial losses for the victim.
Phishing Activity Technical IoCs
The phishing activity begins when the user scans the
QR code embedded in the Word document. This action directs them to the link “hxxp://wj[.]zhvsp[.]com”. This initial URL then redirects to a subdomain, “tiozl[.]cn”, created using a DGA. The use of a DGA means the phishing URLs are constantly changing, making them harder to block preemptively.
[caption id="attachment_77670" align="aligncenter" width="1024"]

Landing page of phishing site (Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The domain “tiozl[.]cn” is hosted on the IP address “20.2.161[.]134”. This IP address is associated with multiple other domains, suggesting a large-scale phishing operation. The domains linked to this campaign are:
- 2wxlrl.tiozl[.]cn
- op18bw[.]tiozl.cn
- gzha31.tiozl[.]cn
- i5xydb[.]tiozl.cn
- hzrz7c.zcyyl[.]com
Further investigation revealed that the SHA-256 fingerprint of an SSH server host key associated with the IP address “20.2.161[.]134” is linked to 18 other IPs, all within the same Autonomous System Number (ASN), AS8075, and located in Hong Kong. These IPs host URLs with similar patterns, indicating a coordinated effort to deploy numerous phishing sites.
The rise in QR code phishing attacks underscores the increasing sophistication and adaptability of cybercriminals. By exploiting the widespread use of QR codes - especially in a post-pandemic world - these attacks effectively lure users into divulging sensitive financial information.
The recent campaign targeting Chinese citizens highlights the severity of this threat, as malicious actors use seemingly official documents to gather card details and passwords, leading to significant financial losses. This trend emphasizes the need for heightened vigilance and robust security measures to protect against such evolving threats.
Recommendations for Mitigation
To mitigate the risk of QR code phishing attacks, CRIL said it is crucial to follow these
cybersecurity best practices:
1. Scan QR codes from trusted sources only: Avoid scanning codes from unsolicited emails, messages, or documents, especially those offering financial incentives or urgent actions.
2. Verify URLs before proceeding: After scanning a QR code, carefully check the URL for legitimacy, such as official domains and secure connections (https://).
3. Install reputable antivirus and anti-phishing software: These tools can detect and block malicious websites and downloads.
4. Stay informed about phishing techniques: Educate yourself and others about the
risks associated with QR codes to prevent successful phishing attacks.
5. Use two-factor authentication (2FA): This adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
6. Keep software up to date: Ensure your operating systems, browsers, and applications are updated with the latest security patches to protect against known
vulnerabilities.
7. Use secure QR code scanner apps: Consider apps that check URLs against a database of known malicious sites before opening them.
8. Monitor financial statements regularly: Review your bank and credit card statements for unauthorized transactions and report any suspicious activity immediately.



















 MS Word file containing QR code (Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The documents are meticulously crafted to look authentic, complete with official logos and language that mimics government communications. Once the QR code in the
MS Word file containing QR code (Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The documents are meticulously crafted to look authentic, complete with official logos and language that mimics government communications. Once the QR code in the  Landing page of phishing site (Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The domain “tiozl[.]cn” is hosted on the IP address “20.2.161[.]134”. This IP address is associated with multiple other domains, suggesting a large-scale phishing operation. The domains linked to this campaign are:
- 2wxlrl.tiozl[.]cn
- op18bw[.]tiozl.cn
- gzha31.tiozl[.]cn
- i5xydb[.]tiozl.cn
- hzrz7c.zcyyl[.]com
Further investigation revealed that the SHA-256 fingerprint of an SSH server host key associated with the IP address “20.2.161[.]134” is linked to 18 other IPs, all within the same Autonomous System Number (ASN), AS8075, and located in Hong Kong. These IPs host URLs with similar patterns, indicating a coordinated effort to deploy numerous phishing sites.
The rise in QR code phishing attacks underscores the increasing sophistication and adaptability of cybercriminals. By exploiting the widespread use of QR codes - especially in a post-pandemic world - these attacks effectively lure users into divulging sensitive financial information.
The recent campaign targeting Chinese citizens highlights the severity of this threat, as malicious actors use seemingly official documents to gather card details and passwords, leading to significant financial losses. This trend emphasizes the need for heightened vigilance and robust security measures to protect against such evolving threats.
Landing page of phishing site (Source: Cyble)[/caption]
The domain “tiozl[.]cn” is hosted on the IP address “20.2.161[.]134”. This IP address is associated with multiple other domains, suggesting a large-scale phishing operation. The domains linked to this campaign are:
- 2wxlrl.tiozl[.]cn
- op18bw[.]tiozl.cn
- gzha31.tiozl[.]cn
- i5xydb[.]tiozl.cn
- hzrz7c.zcyyl[.]com
Further investigation revealed that the SHA-256 fingerprint of an SSH server host key associated with the IP address “20.2.161[.]134” is linked to 18 other IPs, all within the same Autonomous System Number (ASN), AS8075, and located in Hong Kong. These IPs host URLs with similar patterns, indicating a coordinated effort to deploy numerous phishing sites.
The rise in QR code phishing attacks underscores the increasing sophistication and adaptability of cybercriminals. By exploiting the widespread use of QR codes - especially in a post-pandemic world - these attacks effectively lure users into divulging sensitive financial information.
The recent campaign targeting Chinese citizens highlights the severity of this threat, as malicious actors use seemingly official documents to gather card details and passwords, leading to significant financial losses. This trend emphasizes the need for heightened vigilance and robust security measures to protect against such evolving threats.












 Items seized in Ukraine ransomware arrest[/caption]
The Ukraine
Items seized in Ukraine ransomware arrest[/caption]
The Ukraine