
A newly disclosed vulnerability in Progress MOVEit Transfer has sparked concern among cybersecurity experts due to the lingering memory of high-profile attacks by ransomware gangs using
a different vulnerability last year that hit organizations such as the BBC and FBI. The new authentication bypass flaw, officially designated CVE-2024-5806, could potentially allow unauthorized access to sensitive data.
MOVEit Transfer, designed for large-scale enterprise use, boasts features compliant with regulations like PCI and HIPAA. It offers various file transfer methods, including SFTP and HTTPS, making it a critical component in many organizations'
data management infrastructure.
Progress initially kept details of CVE-2024-5806 under wraps, advising customers to patch systems before its disclosure. On June 25th, 2024, Progress officially un-embargoed the vulnerability, revealing that it affects both MOVEit Transfer version 2023.0 and newer, as well as MOVEit Gateway version 2024.0 and newer.
Progress MOVEit Vulnerability Details
WatchTowr Labs was
sent details of the vulnerability by a user who identified as 'dav1d_bl41ne' on its IRC channel, an unusual method of vulnerability sharing, the researchers noted. The researchers decided to investigate further, setting up a test environment to replicate the vulnerability.
[caption id="attachment_79318" align="alignnone" width="471"]

Source: labs.watchtowr.com[/caption]
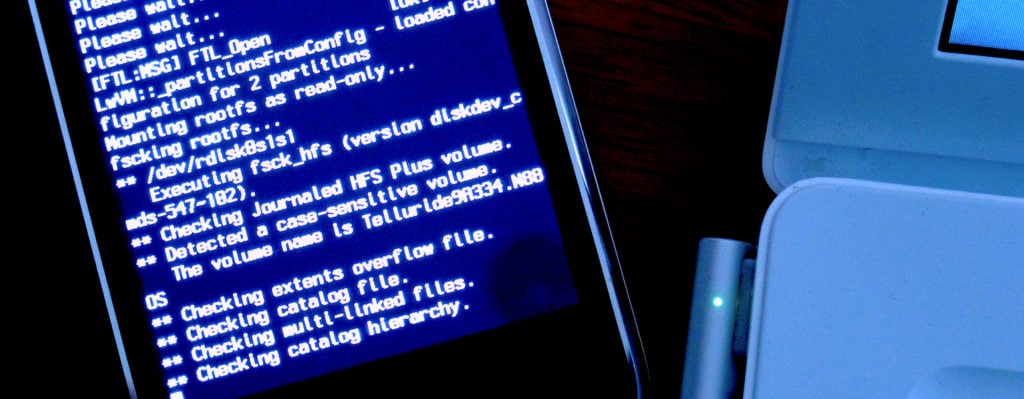
The debugger output from the test environment showed that the server was throwing exceptions and attempting to access files in unexpected ways. Upon further investigation, the researchers discovered that the vulnerability could be exploited by providing a valid file path instead of the SSH public key during authentication. This led to the server attempting to access the file, giving the attacker
unauthorized access to the system.
The researchers shared the following steps on exploiting the vulnerability:
- Upload a public key to the File Transfer server.
- Rather than supplying a legitimate public key, send a file path to the public key, signing the authentication request with the same public key.
- The key will be accepted by the server with successful login, allowing for the access of target files.
The flaw affects MOVEit Transfer versions 2023.0 and newer, as well as MOVEit Gateway 2024.0 and later. Progress
describes it as an "Improper Authentication vulnerability" in the SFTP module that could lead to "Authentication Bypass in limited scenarios." In limited scenarios, CVE-2024-5806 allows for authentication bypass, potentially giving attackers unauthorized access to sensitive files. The vulnerability is particularly concerning because the software is widely used among enterprises, making it a prime target for APT groups, ransomware gangs, and other malicious actors.
Progress has shared the following recommendations to prevent exploitation of the flaw:
- Block public inbound RDP access to MOVEit Transfer server(s).
- Limit outbound access on MOVEit Transfer server(s) to only trusted endpoints.
According to a post on X from The Shadowserver Foundation, the foundation has already observed active exploitation attempts using the vulnerability soon after its disclosure.
[caption id="attachment_79326" align="alignnone" width="1170"]

Source: X.com[/caption]
Implications of the MOVEit Vulnerability
The discovery of this vulnerability soon
after major exploitation last year has reignited discussions about the security of file transfer solutions in enterprise environments. The potential for unauthorized access to sensitive files could have far-reaching consequences for the large number of enterprises that rely on MOVEit Transfer.
While the full extent of the vulnerability's impact is still being assessed, the incident has sparked more debate about responsible disclosure practices in the
cybersecurity community. Some argue that early, private notifications to affected parties are crucial, while others advocate for more transparent, public disclosures to ensure widespread awareness and prompt action.
As the situation develops, IT administrators and
security professionals are advised to stay vigilant, monitor for any signs of exploitation, and implement recommended security measures to protect their MOVEit Transfer deployments.




 Screenshot taken from the livestream.[/caption]
The fake video appears to stem from an edit of a
Screenshot taken from the livestream.[/caption]
The fake video appears to stem from an edit of a  Cryptocurrency addresses involved with the
Cryptocurrency addresses involved with the  Email confirmation of Channel takedown[/caption]
It is unknown if the live transaction feed featured on the scam website reflects actual real-time transactions. The full extent and the victim count from this cryptocurrency scam is unknown; details of the campaign have been sent to
Email confirmation of Channel takedown[/caption]
It is unknown if the live transaction feed featured on the scam website reflects actual real-time transactions. The full extent and the victim count from this cryptocurrency scam is unknown; details of the campaign have been sent to  Screenshot of alleged transactions[/caption]
The campaign highlights the threat of Artificial Intelligence content to election-related processes, legitimate campaign donations and impersonation of candidates or well-known figures. In a recent incident, crypto scammers
Screenshot of alleged transactions[/caption]
The campaign highlights the threat of Artificial Intelligence content to election-related processes, legitimate campaign donations and impersonation of candidates or well-known figures. In a recent incident, crypto scammers 




 Arrested
Arrested 
 Source: labs.watchtowr.com[/caption]
The debugger output from the test environment showed that the server was throwing exceptions and attempting to access files in unexpected ways. Upon further investigation, the researchers discovered that the vulnerability could be exploited by providing a valid file path instead of the SSH public key during authentication. This led to the server attempting to access the file, giving the attacker
Source: labs.watchtowr.com[/caption]
The debugger output from the test environment showed that the server was throwing exceptions and attempting to access files in unexpected ways. Upon further investigation, the researchers discovered that the vulnerability could be exploited by providing a valid file path instead of the SSH public key during authentication. This led to the server attempting to access the file, giving the attacker  Source: X.com[/caption]
Source: X.com[/caption]

 Source: trendmicro.com[/caption]
It linked to a "whitepaper" – a
Source: trendmicro.com[/caption]
It linked to a "whitepaper" – a  Source: trendmicro.com[/caption]
The researchers remarked that AI-generated images are becoming increasingly common in such ICO scams, as they offer a cost-effective and time-efficient way to create convincing lures. Cybercriminals can use AI to generate text, correct spelling and grammatical errors, and even create sentences in languages they do not speak.
[caption id="attachment_79256" align="alignnone" width="384"]
Source: trendmicro.com[/caption]
The researchers remarked that AI-generated images are becoming increasingly common in such ICO scams, as they offer a cost-effective and time-efficient way to create convincing lures. Cybercriminals can use AI to generate text, correct spelling and grammatical errors, and even create sentences in languages they do not speak.
[caption id="attachment_79256" align="alignnone" width="384"] Source: trendmicro.com[/caption]
The researchers spotted at least three other ICO Olympics
Source: trendmicro.com[/caption]
The researchers spotted at least three other ICO Olympics 




 Source: mnews.jtbc.co.kr[/caption]
The malware, which was designed to interfere with BitTorrent traffic, was allegedly used to
Source: mnews.jtbc.co.kr[/caption]
The malware, which was designed to interfere with BitTorrent traffic, was allegedly used to 
 At least 104183 websites might be affected. (Source: publicwww.com)[/caption]
The compromised Polyfill code dynamically generates malware based on HTTP headers, potentially utilizing multiple attack vectors. Researchers from Sansec
At least 104183 websites might be affected. (Source: publicwww.com)[/caption]
The compromised Polyfill code dynamically generates malware based on HTTP headers, potentially utilizing multiple attack vectors. Researchers from Sansec  Source: X.com(@triblondon)[/caption]
[caption id="attachment_79102" align="alignnone" width="634"]
Source: X.com(@triblondon)[/caption]
[caption id="attachment_79102" align="alignnone" width="634"] Source: X.com(@triblondon)[/caption]
Experts have
Source: X.com(@triblondon)[/caption]
Experts have 












 Source: X[/caption]
Source: X[/caption]












