[updated] Federal Reserve “breached” data may actually belong to Evolve Bank
A shockwave went through the financial world when ransomware group LockBit claimed to have breached the US Federal Reserve, the central banking system of the United States.
On LockBit’s dark web leak site, the group threatened to release over 30 TB of banking information containing Americans’ banking data if a ransom wasn’t paid by June 25:

“Federal banking is the term for the way the Federal Bank of America distributes its money. The Reserve operates twelve banking districts around the country which oversee money distribution within their respective districts. The twelve cities which are home to the Reserve Banks are Boston, New York City, Philadelphia, Richmond, Atlanta, Dallas, Saint Louis, Cleveland, Chicago, Minneapolis, Kansas City and San Francisco.
33 terabytes of juicy banking information containing American’s banking secrets.”
The statement ends expressing the group’s disappointment about a negotiator who apparently offered to pay $50,000.
So, you can imagine that everyone was anticipating the end of the countdown that signalled the release of the stolen data with bated breath.
However, when that deadline passed and the data was released, people who looked at the data found it did not, in fact, belong to the Federal Reserve but instead to a particular financial organization: Evolve Bank & Trust.

All the links lead to directories containing data that seems to belong to Evolve.
There hasn’t been enough time to do a full analysis of the huge amount of data, but it appears it is only remotely tied to the Federal Reserve by some included links to a Federal Reserve press link from mid-June.
At that time, the US Federal Reserve Board penalized Evolve Bancorp and its subsidiary, Evolve Bank & Trust, for multiple “deficiencies” in the bank’s risk management, anti-money laundering (AML) and compliance practices.
According to the Federal Reserve statement released at the time:
“In addition, Evolve did not maintain an effective risk management program or controls sufficient to comply with anti-money laundering laws and laws protecting consumers.”
So, as expected, LockBit drew a lot of attention under false pretences.
The group was disrupted by law enforcement in February of 2024 and their activity diminished as a result. As the ThreatDown monthly ransomware review of May review pointed out:
“While LockBit is technically still alive, it’s fair to say the group is not what it was: Not only are its attacks dwindling, but in early May law enforcement also revealed the identity of alleged LockBit leader Dmitry Khoroshev, aka LockBitSupp. LockBitSupp, who is now subjected to a series of asset freezes and travel bans, also has a reward of up to $10 million over his head for information that leads to his arrest.”
And recently the FBI announced it had over 7,000 LockBit decryption keys in its possession, allowing it to help victims to recover data encrypted by the gang in past attacks. LockBit ransomware has impacted over 1,800 US victims, according to FBI stats.
Back to the data, it’s good news it appears not to be from the Federal Reserve. However, it’s not good news for customers of Evolve Bank & Trust and their data may well have been stolen and published. And it’s a lot of data.
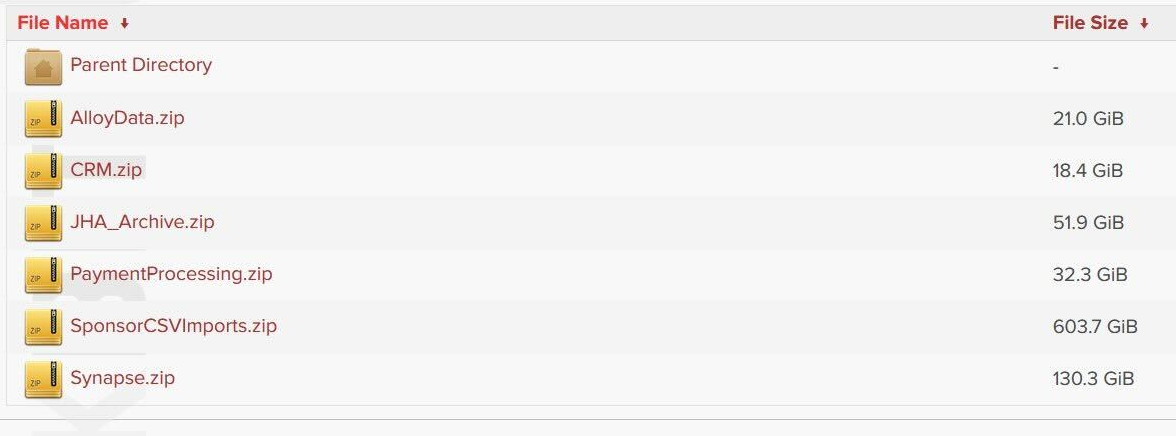
Update June 28, 2024
Mercury has notified customers that the data stolen from Evolve Bank & Trust, included some account numbers, deposit balances, business owner names, and emails associated with Mercury and other fintech accounts.
“Affected Mercury customers have been notified of the breach and the preventative steps we are taking to keep customer funds secure.”
It is as of yet unknown which “other fintech accounts” may be involved. We’ll keep you updated on this developing story. For now, there’s no official statement from Evolve, but there are general things to know if you think you have been involved in a data breach.
Protecting yourself after a data breach
There are some actions you can take if you are, or suspect you may have been, the victim of a data breach.
- Check the vendor’s advice. Every breach is different, so check with the vendor to find out what’s happened, and follow any specific advice they offer.
- Change your password. You can make a stolen password useless to thieves by changing it. Choose a strong password that you don’t use for anything else. Better yet, let a password manager choose one for you.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA). If you can, use a FIDO2-compliant hardware key, laptop or phone as your second factor. Some forms of two-factor authentication (2FA) can be phished just as easily as a password. 2FA that relies on a FIDO2 device can’t be phished.
- Watch out for fake vendors. The thieves may contact you posing as the vendor. Check the vendor website to see if they are contacting victims, and verify the identity of anyone who contacts you using a different communication channel.
- Take your time. Phishing attacks often impersonate people or brands you know, and use themes that require urgent attention, such as missed deliveries, account suspensions, and security alerts.
- Consider not storing your card details. It’s definitely more convenient to get sites to remember your card details for you, but we highly recommend not storing that information on websites.
- Set up identity monitoring. Identity monitoring alerts you if your personal information is found being traded illegally online, and helps you recover after.
Check your digital footprint
Malwarebytes has a new free tool for you to check how much of your personal data has been exposed online. Submit your email address (it’s best to give the one you most frequently use) to our free Digital Footprint scan and we’ll give you a report and recommendations.
We don’t just report on threats – we help safeguard your entire digital identity
Cybersecurity risks should never spread beyond a headline. Protect your—and your family’s—personal information by using identity protection.